1) EXEC: launch the New OpenShift Application wizard and create a new OpenShift application that you import to your workspace. (ex. call the applicatino as)
2) ASSERT: Your application gets imported to your workspace (ex. project as)
3) EXEC: delete the new project, kill the OpenShift application
4) EXEC: create the very same application again and have it imported to your workspace
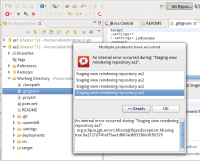
5) EXEC: Go to the Git Perspective and double click some file, so that it gets opened in a editor. You'll very soon get the following error:
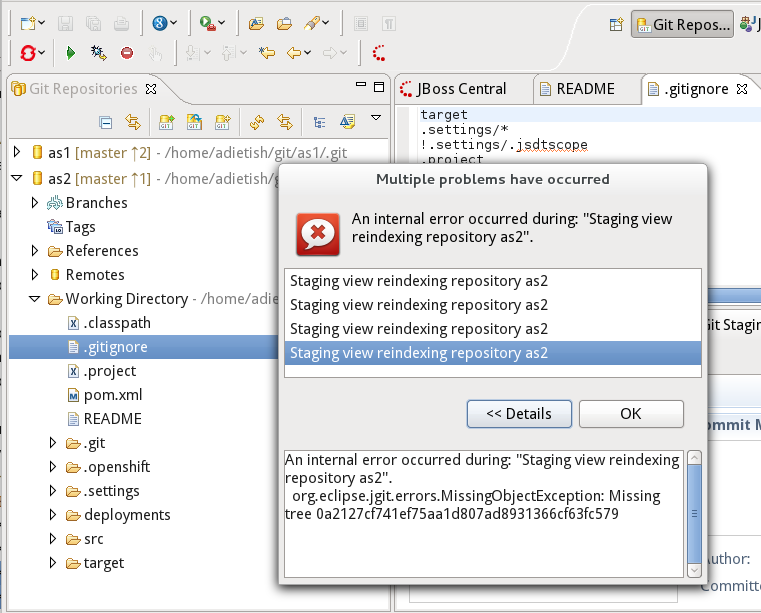
6) EXEC: Go to the command-line and do git fsck.
Result:
You'll spot something very similar to this:
[adietish@adietish-thinkpad as2]$ git fsck
broken link from commit 6410005677d35ea202df51097c4077f36d8b9ac1
to tree 0a2127cf741ef75aa1d807ad8931366cf63fc579
missing tree 0a2127cf741ef75aa1d807ad8931366cf63fc579
missing blob ef669b78c38fa1317bc89d5d93cd3205c615130f
Interesting enough, .gitignore is now a new file in the git repo even though this is completely erroneous. .gitignore was cloned, we only modified it by adding some further entries (.settings, .classpath, .project, etc.):
[adietish@adietish-thinkpad as2]$ git status
# On branch master
# Your branch is ahead of 'origin/master' by 1 commit.
#
# Changes to be committed:
# (use "git reset HEAD <file>..." to unstage)
#
# new file: .gitignore
ALTERNATIVE:
1) EXEC: launch the New OpenShift Application wizard and create a new OpenShift application that you import to your workspace. (ex. call the applicatino as)
2) ASSERT: Your application gets imported to your workspace (ex. project as)
3) EXEC: delete the new project
4) EXEC: Reimport the application from OpenShift to your workspace
6) EXEC: Go to the command-line and do git fsck.
Result:
You'll spot something very similar to this:
git fsck
broken link from commit 74682dc05a4085a4165ef1a280129e9a9c5d412f
to tree 9b742cf75471e6505b5ce7272104f34064326194
missing tree 9b742cf75471e6505b5ce7272104f34064326194
missing blob ef669b78c38fa1317bc89d5d93cd3205c615130f
ALTERNATIVE that does not involve using OpenShift:
1) EXEC: create a new java project (ex. test-project)
2) EXEC: share this project with egit: Team->Share Project->Git->Create
3) EXEC: Commit new file (test) to repo: Team->Commit->check ".classpath"
4) EXEC: Delete project in Eclipse, kill Repository-Folder in File-Explorer / CLI
5) EXEC: Repeat steps 1-4
6) Go to CLI and cd to the git repo. Then do: git fsck
Result:
You'll spot something very similar to this:
git fsck
broken link from commit 74682dc05a4085a4165ef1a280129e9a9c5d412f
to tree 9b742cf75471e6505b5ce7272104f34064326194
missing tree 9b742cf75471e6505b5ce7272104f34064326194
missing blob ef669b78c38fa1317bc89d5d93cd3205c615130f
Bug
Critical
JBIDE-12301 OpenShift server adapter fails to publish recreated project
JBIDE-12138 serveradapter is git forcing without asking when error occurs in normal git commit
JBIDE-11702 .gitignore cannot exclude .jsdtscope nor factorypath by default