-
Bug
-
Resolution: Done
-
Major
-
2.15.4.GA, 3.1.0.GA
-
False
-
-
False
-
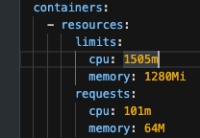
The documentation [1] includes section 5.2.3. (Using a custom plug-in registry for your IDE) and others that hint that using .che/che-editor.yaml can allow the user to influence things like memory limits. This does not seem to be true.