-
Epic
-
Resolution: Done
-
Blocker
-
None
-
RFE Automatic Spoke registration in ACM
-
False
-
-
False
-
Green
-
To Do
-
TELCOSTRAT-54 - RAN Integration
-
0% To Do, 0% In Progress, 100% Done
OCP/Telco Definition of Done
Epic Template descriptions and documentation.
ACM-wide Product Requirements (Top-level Epics).{}
Epic Goal
- Provide a mechanism for automatic registration of relocatable clusters to ACM. The registration process must be initiated on first boot, and be carried out in a fully automated, unattended fashion.
Why is this important?
- Customers need to deploy SNO clusters in large quantities for Edge environments. This is done in factories where ACM is used to mass-produce generic SNO clusters. Once produced and shipped to the remote Edge site, SNO clusters receive a unique identity and register to Customer’s ACM (e.g. located in service provider’s data center) for management. (The Customer’s ACM is different from Factory ACM).
- ACM supports importing an existing cluster for management. However, this is a manual procedure that requires actions to be performed on both the ACM Hub cluster and the Spoke cluster, using either the web console or the CLI. This RFE is to automate the complete Spoke-to-Hub registration flow in order to support deployments of clusters in Edge environments.
- Importing Edge clusters manually is not feasible due to the large number of clusters produced.
Scenarios
Automatic registration of relocatable clusters
A relocatable cluster is a cluster that has been provisioned in one place (e.g. in a factory) and then is moved to a remote site. The cluster needs to be able to register to a target ACM instance once the cluster is powered on.
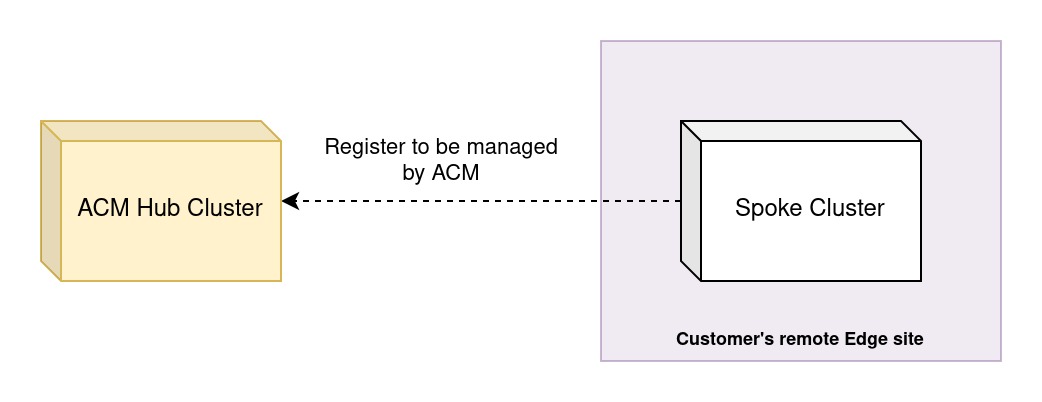
A Spoke cluster that leaves the factory should be able to register on its own, without the need for manual intervention. See the diagram below for a detailed overview of the lifecycle of relocatable CPE (Customer Premise Equipment) Spoke clusters.
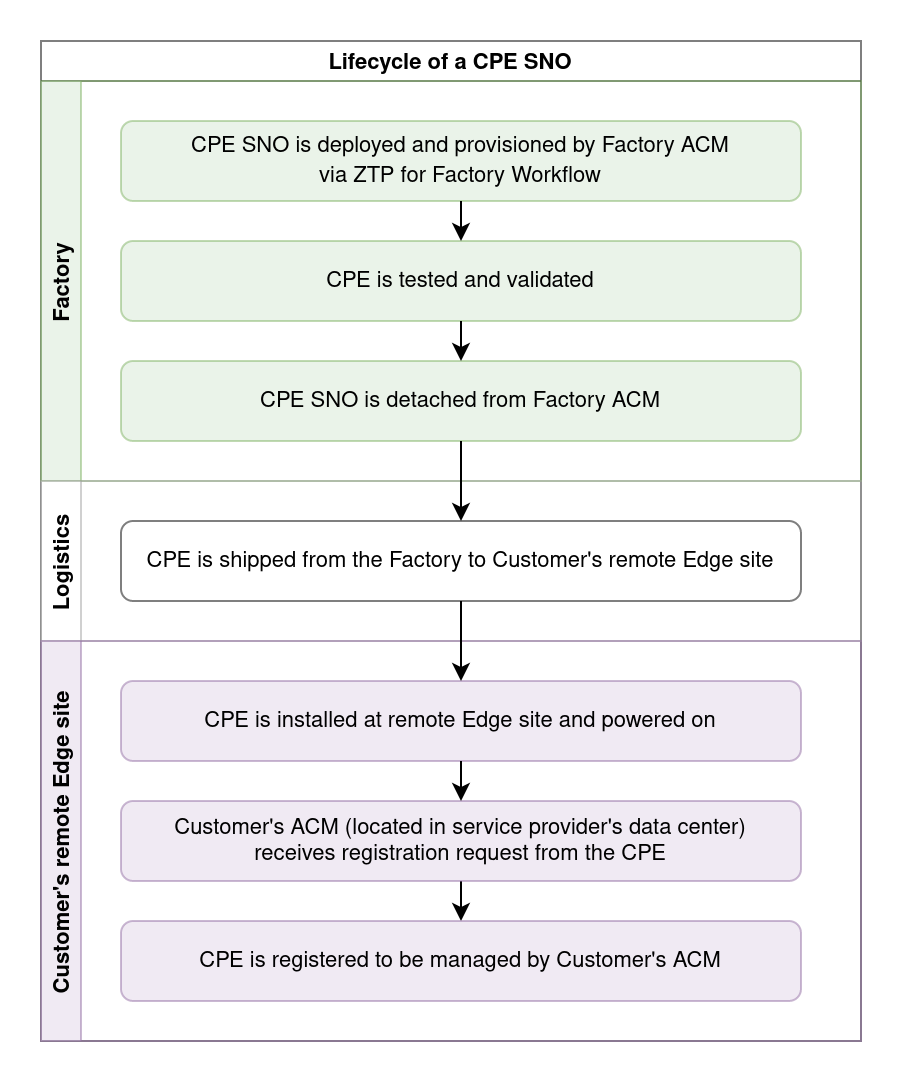
Use case
- Factory ACM provisions a generic CPE SNO cluster in the Factory
- Once the CPE is fully provisioned, the CPE is detached from the Factory ACM
- CPE is tested to verify that it fulfills acceptance criteria and can be shipped to the Customer
- CPE is shipped and installed at Customer’s remote Edge site
- (optional) IPSec tunnel is established with Customer’s ACM site
- CPE receives a unique domain alias and a URL to Customer’s ACM from Customer’s Backend Service
- CPE registers with Customer’s ACM using the domain alias
- (optional) Customer’s ACM checks that the CPE is present on a list of allowed clusters and that the registration request can be processed
- CPE is configured to be managed by Customer’s ACM
Acceptance Criteria
- CI - MUST be running successfully with tests automated
- Release Technical Enablement - Provide necessary release enablement details and documents.
- ...
Dependencies (internal and external)
- ...
Previous Work (Optional):
- An MVP solution for this problem has been developed by the Telco Solutions team, and successfully tested by the partner.
Open questions:
- …
Done Checklist
- CI - CI is running, tests are automated and merged.
- Release Enablement <link to Feature Enablement Presentation>
- DEV - Upstream code and tests merged: <link to meaningful PR or GitHub Issue>
- DEV - Upstream documentation merged: <link to meaningful PR or GitHub Issue>
- DEV - Downstream build attached to advisory: <link to errata>
- QE - Test plans in Polarion: <link or reference to Polarion>
- QE - Automated tests merged: <link or reference to automated tests>
- DOC - Downstream documentation merged: <link to meaningful PR>
- is related to
-
ACM-3405 RFE Apply cluster attributes to generic OCP during initial bringup
-
- Closed
-